What Is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer is a serious condition that affects the tissues in the mouth or throat. It can develop in the tongue, lips, gums, roof of the mouth, or other areas of the mouth. While the causes of oral cancer aren’t yet fully understood, it’s known that certain factors can increase the risk of developing the disease, such as tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and exposure to the human papillomavirus (HPV).
The Importance of Yearly Oral Cancer Screenings
Yearly screenings are crucial for the early detection and treatment of oral cancers. Like other types of cancer, oral cancer can be more effectively treated when it’s caught early. Unfortunately, oral cancer is often not detected until it has reached an advanced stage, which can make it more difficult to treat and lower the chances of survival.
The American Cancer Society recommends that individuals receive oral cancer screenings as part of their routine dental checkups. This can help to detect any first signs and symptoms of oral cancer early on, increasing the chances of successful treatment.
How Dental Cleanings Can Aid in Detecting Oral Cancer Signs
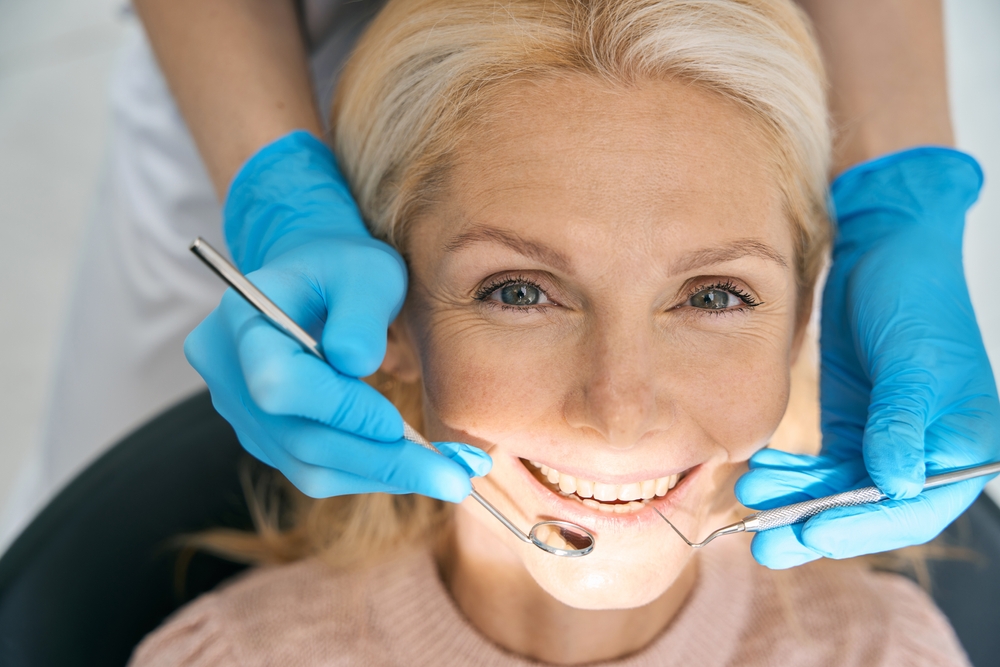
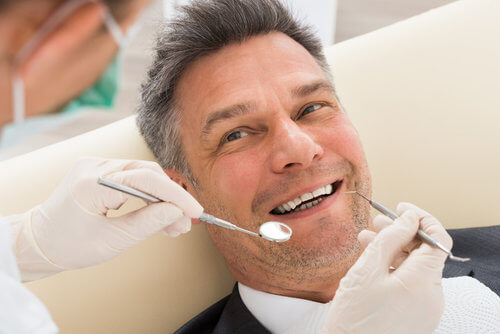
Regular dental cleanings can play an important role in the detection of oral cancer. During a dental cleaning, your dentist will perform an oral cancer screening. They’ll examine the mouth for any signs of cancer, such as red or white patches, sores, or lumps. They may also ask about any symptoms or changes that the patient has noticed in their mouth, such as any mouth pain, difficulty swallowing, or changes in their voice.
In addition to a visual examination, your dentist may also use special tools to detect abnormalities in the tissues of the mouth, throat, head, and neck. This can include using a tongue depressor to view the back of the mouth and a dental mirror to check the sides of the tongue.
If any abnormalities are found, your dentist may perform further testing, such as a biopsy or imaging tests, to determine if cancer is present.
Causes of Oral Cancers
The exact causes of oral cancer aren’t known, but several factors can increase the risk of developing this type of cancer. Some of the common risk factors include:
- Tobacco use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, as well as using smokeless tobacco products, greatly increases the risk of developing oral cancers.
- Alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of developing oral cancers. The risk is even higher for individuals who both smoke and drink alcohol.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV): Certain types of HPV, a sexually transmitted infection, have been linked to an increased risk of oropharyngeal cancer.
- Age: Oral cancers are more common in individuals over the age of 45, although they can occur at any age.
- Sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can increase the risk of lip cancer.
- Poor oral hygiene: Poor oral hygiene, such as infrequent brushing and flossing, can increase the risk of oral cavity cancer.
- Family history: Individuals with a family history of oral cancer may be at an increased risk.
Oral Cancer Treatments
Treatment options for oral cancer may vary depending on the stage of the disease and the individual’s overall health. The most common ways to treat oral cancer include:
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the cancerous tissues in the mouth or throat. This may involve removing part or all of the affected tissue, as well as nearby lymph nodes.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with surgery or chemotherapy.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. It may be used alone or in combination with radiation therapy.
- Targeted Therapy: Uses drugs that target specific molecules in cancer cells to block their growth and spread. Targeted therapy may be used in combination with other oral cancer treatments.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It’s still being studied for the treatment of oral cancer but has shown promise in clinical trials.
- Palliative Care: Palliative care focuses on relieving symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals with advanced oral cancer. This may include pain management, nutritional support, and emotional and spiritual support.
Oral cancer treatment is highly individualized. The best approach will depend on the individual’s overall health, the stage of cancer, cancer’s location, and other factors. Discuss all treatment options with a healthcare professional to determine the treatment plan for you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can oral cancer be prevented?
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent developing oral cancer, there are several steps you can take to reduce your mouth cancer risk. This includes avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining good oral hygiene habits, and getting regular oral cancer screenings.
How often should I receive an oral cancer screening?
The American Cancer Society recommends that individuals receive an oral cancer screening as part of their routine dental checkup at least once a year. However, your dental professional may recommend more frequent screenings based on your risk factors and medical history.
What age should oral cancer screenings start?
The American Cancer Society recommends that oral cancer screenings should start at age 18 for all individuals, regardless of their risk factors. Regular oral cancer screenings should be a part of routine dental checkups and exams.
However, individuals who have a higher risk of developing oral cancer, such as those who use tobacco products, consume excessive alcohol, have a family history of oral cancer, or have been exposed to the human papillomavirus (HPV), may need to start oral cancer screenings earlier and more frequently.
At what site is oral cancer likely to appear?
Oral cavity and oropharyngeal cancers are most frequently found in specific areas of the mouth and throat. The tongue is the most common site, followed by the tonsils and oropharynx (the back of the throat behind the mouth).
Other areas that are commonly affected include the gums, the floor of the mouth, and other parts of the oral cavity. Early detection of mouth cancers through regular screenings and prompt medical attention for any suspicious symptoms is crucial for the effective treatment and management of these cancers.
Schedule Your Visit Today!
If you have concerns about oral cancer or have not received an oral cancer screening as part of your routine dental checkup, we encourage you to schedule an appointment with your local dentist today. Early detection and treatment are key to improving outcomes for individuals with oral cancer. Don’t wait, take action and schedule your mouth cancer screening today with our Staten Island dentists.

Insurance
We accept many insurances. Please contact one of our Insurance Coordinators to discuss your dental coverage plan.
(718) 948 5111
appointments@sidental.com
Open 7 days a week
Reviews
The dentists are absolutely excellent…
“I have been going here for years. The dentists are absolutely excellent and they always have an appointment available that fits into a busy schedule. I also completed invisilgn and my teeth are perfectly straight now. They also practice preventive medicine and just went in for my 6 month cleaning. Every time feel like I have a new set of choppers and best yet the check up noted no cavities!.”
— J.R
Pleasant visit
“As usual, it was a pleasant visit thanks to Dr. Nasso and her great staff..”
— C.M.
Always treated with courtesy and respect.
“Always treated with courtesy and respect. All of my questions were answered regarding upcoming treatments..”
— J.C.
Smile Profile
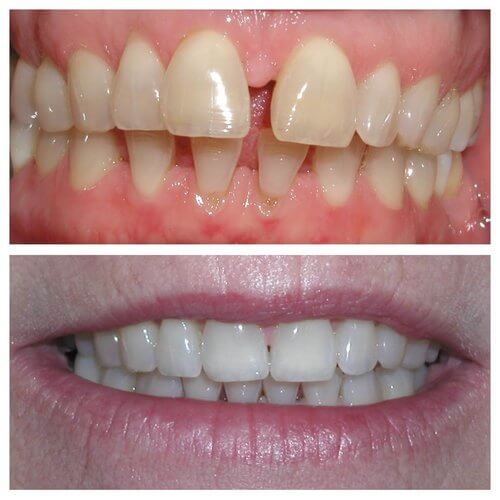
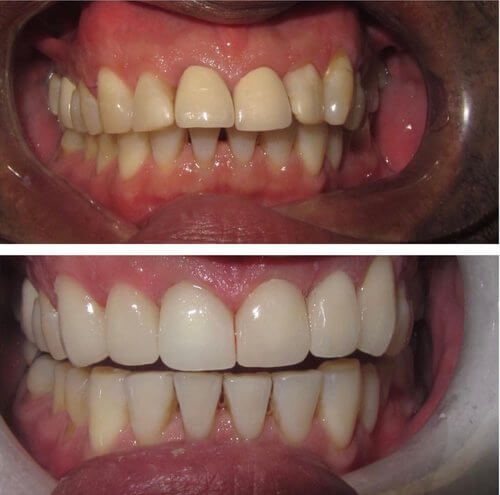
Put your best face forward.
Create a positive change to your teeth and your smile.
