What Is Degenerative Joint Disease?
Degenerative joint disease, also known as osteoarthritis, occurs when the protective cartilage in a joint begins to wear down. It can happen because of normal wear and tear, aging, or an injury. With TMJ, degenerative joint disease can cause the cartilage that cushions the joint to break down, leading to bone-on-bone contact and inflammation. This can cause pain, stiffness, and limited mobility in the jaw.
Causes of Degenerative Joint Disease
Several factors can contribute to the development of degenerative joint disease in TMJ, including:
- Aging: As we age, the cartilage in our joints can naturally break down, leading to degenerative joint disease.
- Injury: Trauma to the jaw, such as a dislocation or a fracture, can increase the risk of developing degenerative joint disease.
- Jaw Overuse: Using the jaw excessively, such as chewing gum or clenching the teeth, can put added stress on the TMJ and increase the risk of developing degenerative joint disease.
- Genetics: Some people may be more predisposed to developing degenerative joint disease due to genetics.
Degenerative Joint Disease Symptoms
Symptoms of degenerative joint disease in the TMJ vary from person to person. Some common symptoms include:
- Pain or tenderness in the jaw joint
- Difficulty opening or closing the mouth
- Clicking, popping, or grinding sounds when moving the jaw
- Stiffness in the jaw muscles
- Headaches
- Earaches
- Tiredness or discomfort in the facial muscles
If you suspect you have degenerative joint disease, contact our Staten Island office to schedule an appointment with one of our dentists.
Who Can Get Degenerative Joint Disease?
Degenerative joint disease, also known as osteoarthritis, is a common condition that can affect anyone, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing this condition:
- Age is a significant risk factor for degenerative joint disease, especially for people over 65, due to wear and tear on the joints over time, which can lead to degeneration and damage.
- Gender also plays a role, as women are more likely than men to develop osteoarthritis, especially in the hands and knees.
- Obesity is another risk factor, as the additional weight places extra stress on the joints, increasing the risk of damage and degeneration.
- Joint injuries, such as those sustained in sports or accidents, can increase the risk of developing degenerative joint disease later in life.
- Certain genetic factors may play a role in the development of osteoarthritis, as people with a family history of the condition may be more likely to develop it themselves.
Degenerative Joint Disease Treatments
There are several treatment options available for degenerative joint disease. These include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, may help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Prescription medications, such as muscle relaxants or corticosteroids, may also be prescribed in some cases.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and stretches can help strengthen the muscles around the jaw joint and improve mobility.
- Splints or Oral Appliances: Wearing a splint or oral appliance can help reduce stress on the TMJ and prevent further damage.
- Jaw Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joint tissue.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can degenerative joint disease be prevented?
While degenerative joint disease cannot be entirely prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing the condition. Maintaining a healthy weight, practicing good posture, avoiding excessive jaw movements, and wearing a mouthguard during high-impact activities can help protect your TMJ and reduce your risk of degenerative joint disease.
Is degenerative joint disease a common condition?
Yes, degenerative joint disease in the TMJ is a relatively common condition, especially in older adults. It’s estimated that around 10 million people in the United States are affected by TMJ disorders, including degenerative joint disease.
How is degenerative joint disease in the TMJ diagnosed?
Degenerative joint disease in TMJ is diagnosed through physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI. Blood tests may also be ordered to rule out other conditions that could be causing your symptoms.
What are the risk factors for developing degenerative joint disease?
Some risk factors for developing degenerative joint disease in TMJ include aging, prior jaw injury or trauma, genetics, and certain medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis. Other factors such as poor posture, teeth grinding or clenching, and excessive gum chewing may also contribute to the development of degenerative joint disease in TMJ.
Find Relief for Degenerative Joint Disease Symptoms
If you’re experiencing jaw pain, stiffness, or limited mobility, see a doctor or dentist for an evaluation. Degenerative joint disease can be a chronic and debilitating condition, but with proper treatment and management, you can improve your quality of life and reduce your symptoms.
Don’t hesitate to seek help and take action to address your TMJ symptoms. Contact your healthcare provider today to schedule an appointment and get started on your path to relief. If you live in the Staten Island area, contact our dentists today to learn more about the TMJ.



Insurance
We accept many insurances. Please contact one of our Insurance Coordinators to discuss your dental coverage plan.
(718) 948 5111
appointments@sidental.com
Open 7 days a week
Reviews
The dentists are absolutely excellent…
“I have been going here for years. The dentists are absolutely excellent and they always have an appointment available that fits into a busy schedule. I also completed invisilgn and my teeth are perfectly straight now. They also practice preventive medicine and just went in for my 6 month cleaning. Every time feel like I have a new set of choppers and best yet the check up noted no cavities!.”
— J.R
Pleasant visit
“As usual, it was a pleasant visit thanks to Dr. Nasso and her great staff..”
— C.M.
Always treated with courtesy and respect.
“Always treated with courtesy and respect. All of my questions were answered regarding upcoming treatments..”
— J.C.
Smile Profile
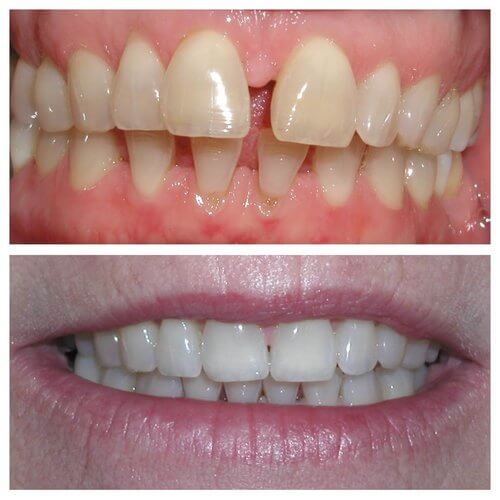
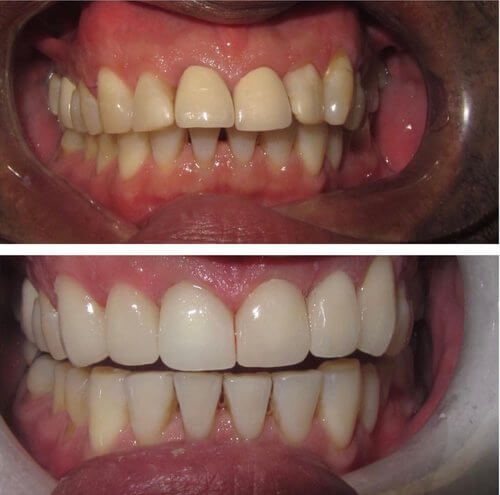
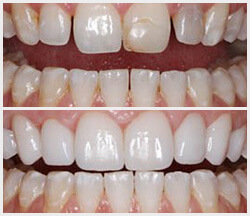
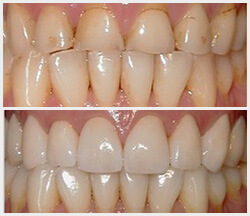
Put your best face forward.
Create a positive change to your teeth and your smile.
